| 作者/單位: | 洪明奇/校長 |
| 期刊名稱: | ACS SENSORS |
| IF值: | 6.944 |
| 領域排名: | CHEMISTRY, ANALYTICAL (4/84) 4.8% |
| 文章摘要: |
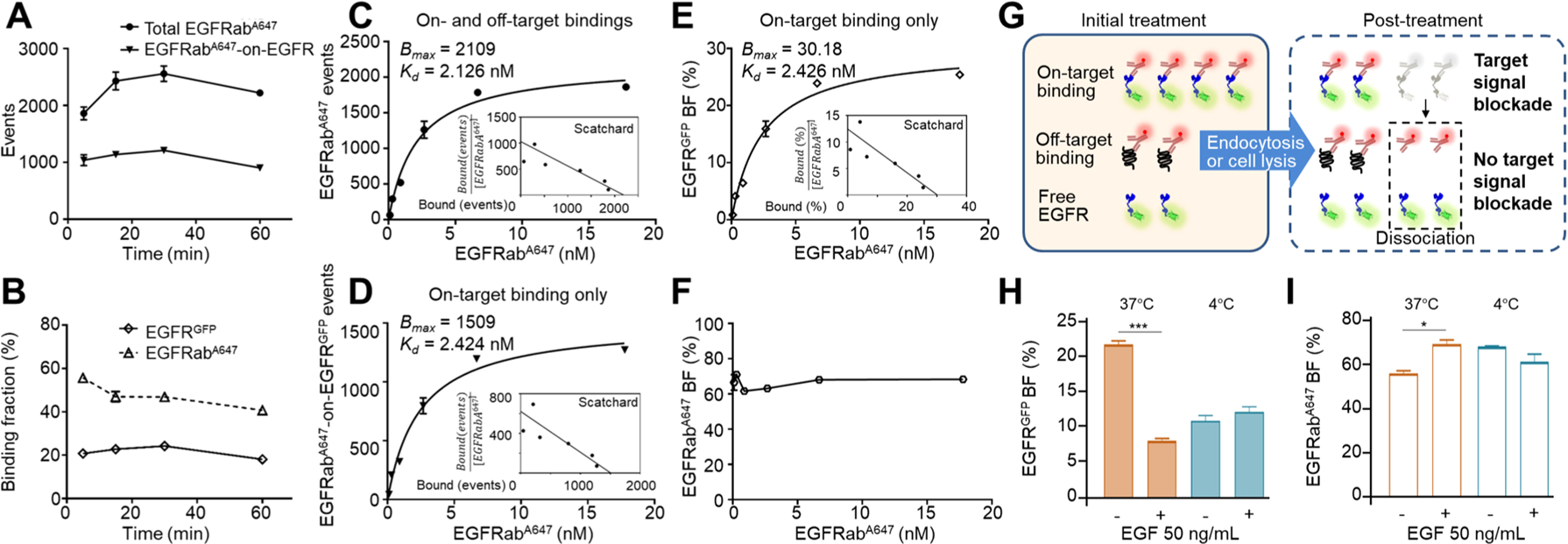
While monoclonal antibodies are the fastest-growing class of therapeutic agents, we lack a method that can directly quantify the on- and off-target binding affinities of newly developed therapeutic antibodies in crude cell lysates. As a result, some therapeutic antibody candidates could have a moderate on-target binding affinity but a high off-target binding affinity, which not only gives a reduced efficacy but triggers unwanted side effects. Here, we report a single-molecule counting method that precisely quantifies antibody-bound receptors, free receptors, and unbound antibodies in crude cell lysates, termed digital receptor occupancy assay (DRO). Compared to the traditional flow cytometry-based binding assay, DRO assay enables direct and digital quantification of the three molecular species in solution without the additional antibodies for competitive binding. When characterizing the therapeutic antibody, cetuximab, using DRO assay, we found the on-target binding ratio to be 65% and the binding constant (Kd) to be 2.4 nM, while the off-target binding causes the binding constant to decrease by 0.3 nM. Other than cultured cells, the DRO assay can be performed on tumor mouse xenograft models. Thus, DRO is a simple and highly quantitative method for cell-based antibody binding analysis which can be broadly applied to screen and validate new therapeutic antibodies. |
發表者簡介
 |
| 單位:校長室 校長 |
|
研究專長:
|