| 作者/單位: | 王志豪/生物醫學研究所 |
| 期刊名稱: | SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE |
| IF值: | 16.304 |
| 領域排名: | MEDICINE, RESEARCH & EXPERIMENTAL (2/139) 1.4% |
| 文章摘要: |
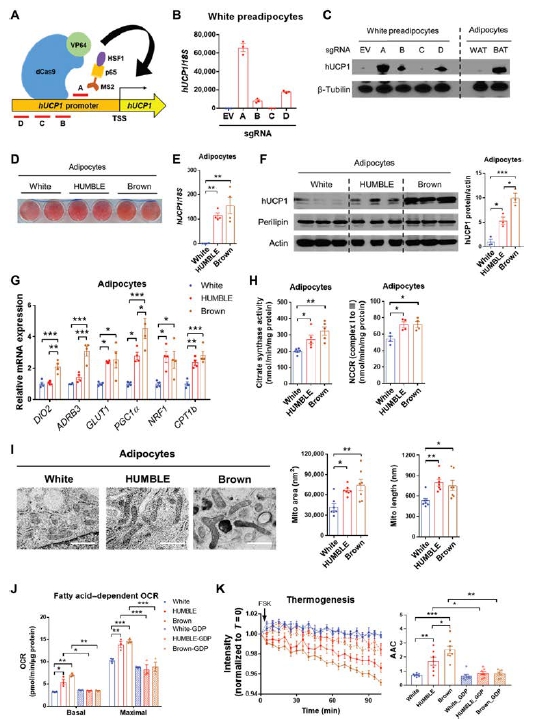
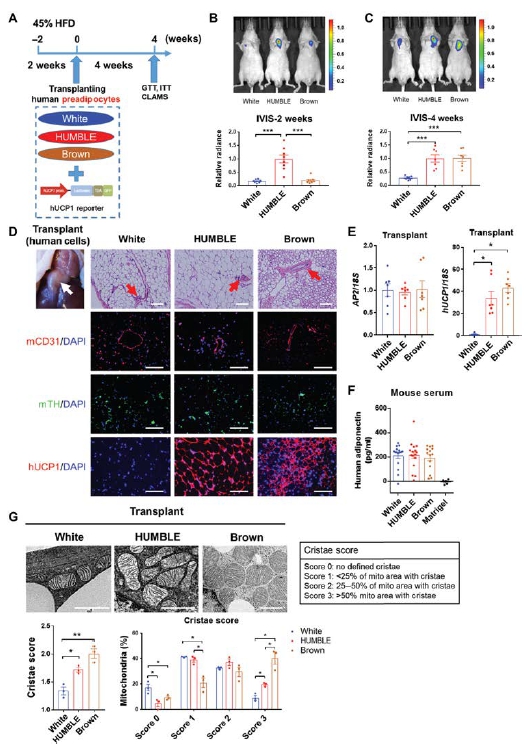
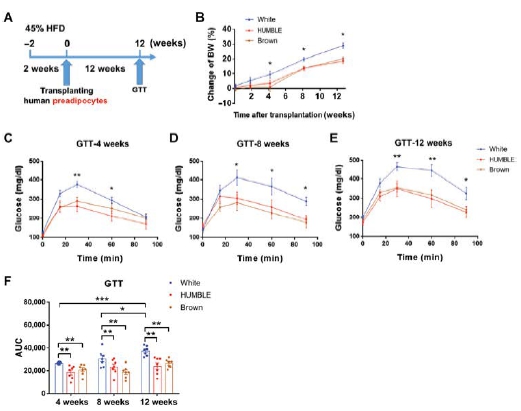
Brown and brown-like beige/brite adipocytes dissipate energy and have been proposed as therapeutic targets to combat metabolic disorders. However, the therapeutic effects of cell-based therapy in humans remain unclear. Here, we created human brown-like (HUMBLE) cells by engineering human white preadipocytes using CRISPR-Cas9-SAM-gRNA to activate endogenous uncoupling protein 1 expression. Obese mice that received HUMBLE cell transplants showed a sustained improvement in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, as well as increased energy expenditure. Mechanistically, increased arginine/nitric oxide (NO) metabolism in HUMBLE adipocytes promoted the production of NO that was carried by S-nitrosothiols and nitrite in red blood cells to activate endogenous brown fat and improved glucose homeostasis in recipient animals. Together, these data demonstrate the utility of using CRISPR-Cas9 technology to engineer human white adipocytes to display brown fat-like phenotypes and may open up cell-based therapeutic opportunities to combat obesity and diabetes. |
發表者簡介
 |
| 單位:醫學院生物醫學研究所 助理教授 |
|
研究專長:
|
|
Read More |