| 作者/單位: | 洪明奇/校長 |
| 期刊名稱: | NATURE CELL BIOLOGY |
| IF值: | 20.042 |
| 領域排名: | CELL BIOLOGY (8/195) 4.1% |
| 文章摘要: |
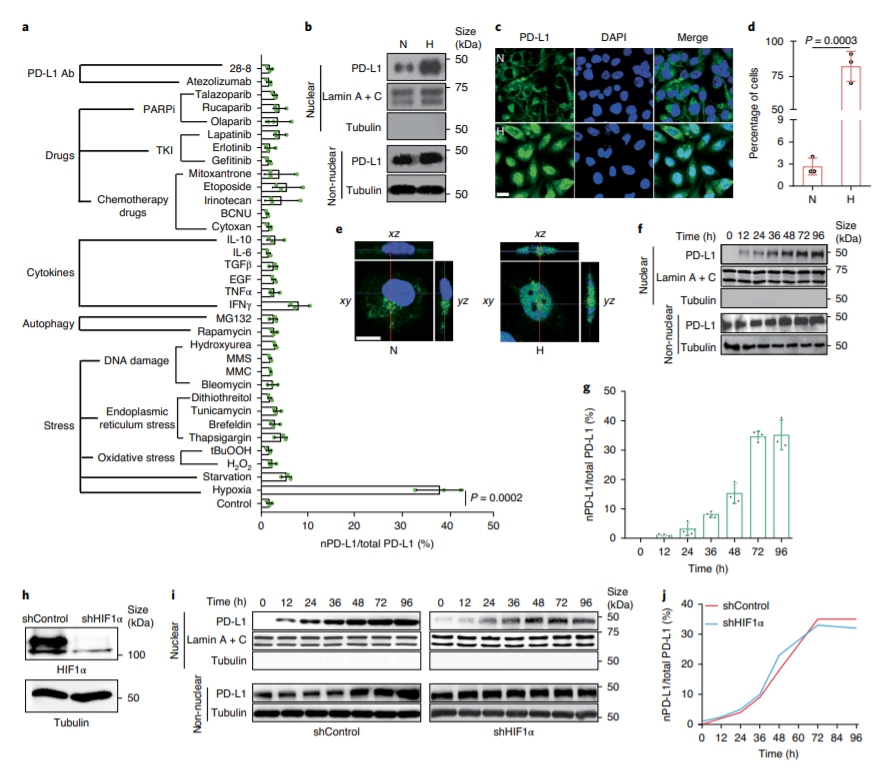
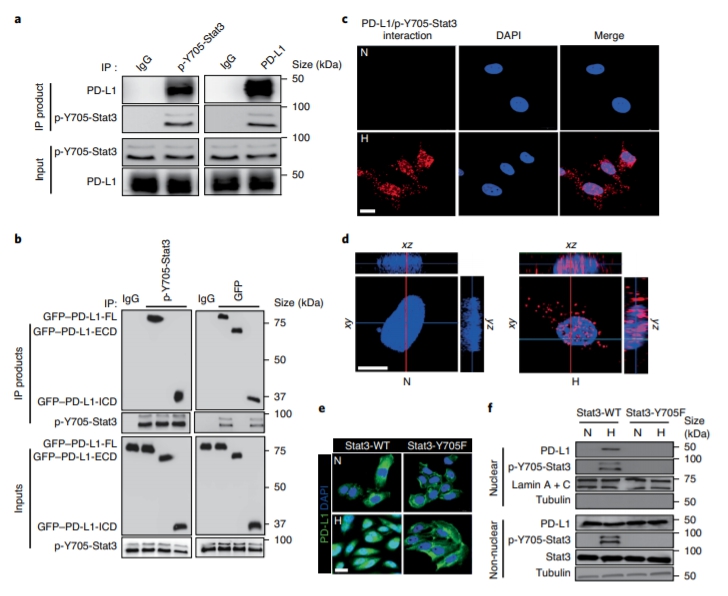
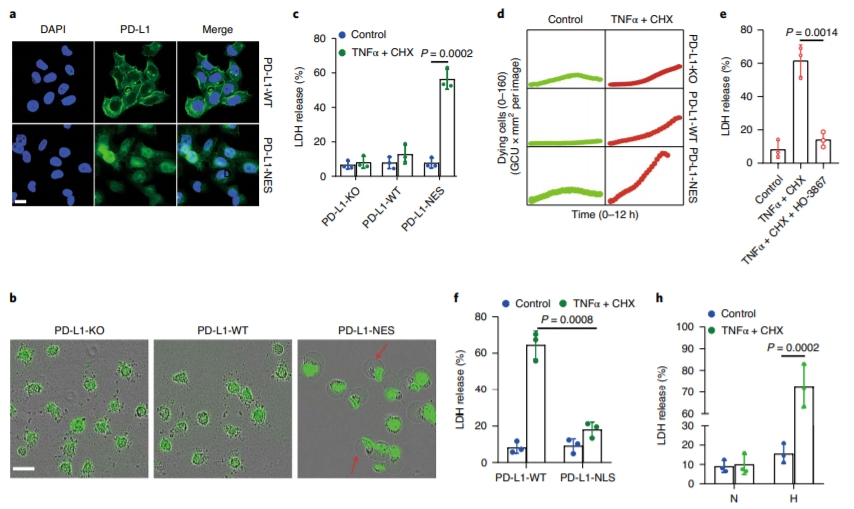
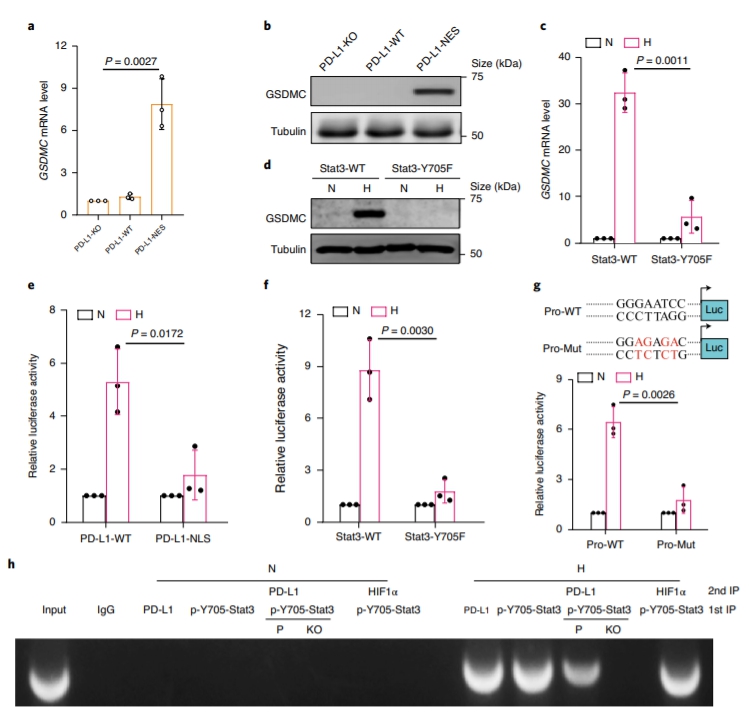
Although pyroptosis is critical for macrophages against pathogen infection, its role and mechanism in cancer cells remains unclear. PD-L1 has been detected in the nucleus, with unknown function. Here we show that PD-L1 switches TNF alpha-induced apoptosis to pyroptosis in cancer cells, resulting in tumour necrosis. Under hypoxia, p-Stat3 physically interacts with PD-L1 and facilitates its nuclear translocation, enhancing the transcription of thegasdermin C(GSDMC) gene. GSDMC is specifically cleaved by caspase-8 with TNF alpha treatment, generating a GSDMC N-terminal domain that forms pores on the cell membrane and induces pyroptosis. Nuclear PD-L1, caspase-8 and GSDMC are required for macrophage-derived TNF alpha-induced tumour necrosis in vivo. Moreover, high expression of GSDMC correlates with poor survival. Antibiotic chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis in breast cancer. These findings identify a non-immune checkpoint function of PD-L1 and provide an unexpected concept that GSDMC/caspase-8 mediates a non-canonical pyroptosis pathway in cancer cells, causing tumour necrosis. Hou et al. show that following hypoxia PD-L1 translocates into the nucleus to enhance transcription of GSDMC, which is then cleaved and activated by caspase-8 to cause pyroptosis in cancer cells. |
發表者簡介
 |
| 單位:校長室 校長 |
|
研究專長:
|